Risk Management In Banking [Complete Guide]
Last Updated: September 19, 2023
Risk Management in Banking: Introduction
The Great Depression spawned the most ambitious legislative program ever attempted by the United States: The New Deal. The New Deal created an environment where the federal government accepted responsibility for a variety of issues originally left to individuals, states, and city governments. This unprecedented increase in federal initiatives resulted in the enactment of a myriad of bureaucratic agencies. These various agencies were all denominated by their titles’ acronyms, creating notorious confusion around who was in charge of what. This led U.S. citizens to use the term “alphabet soup” when describing these regulatory bodies.
Alphabet soup has become a widely used metaphor to refer to an abundance of incomprehensible language containing abbreviations. Most organizations that operate today must adhere to the rules of various regulating bodies. Some industries, however, are required to adhere to more than others – like the banking industry. Banks are highly regulated in order to promote financial stability, foster competition, and protect consumers. Due to the strictly monitored environment in which banks operate, it’s critical that they have strategies in place to keep all their ducks in a row.
Risk management is an essential piece of banking operations. To demonstrate why, this guide will provide an overview of risk management in banking, discuss specifically the types of risk management in commercial banks, detail risk management practices in banks, go over the process of risk management in banks, and explain how to use enterprise risk management software for banks.
Risk Management in Banking Overview
Just like any business, banks face a myriad of risks. However, given how important the banking sector is and the government’s stake in keeping risks in check, the risks weigh heavier than they do on most other industries. There are various types of risks that a bank may face and is important to understand how banks manage risk.
Types of Risk Management in Commercial Banks
Banking Risk Type #1: Credit Risk
Banks often lend out money. The chance that a loan recipient does not pay back that money can be measured as credit risk. This can result in an interruption of cash flows, increased costs for collection, and more.
Banking Risk Type #2: Market Risk
This refers to the risk of an investment decreasing in value as a result of market factors (such as a recession). Sometimes this is referred to as “systematic risk.”
Banking Risk Type #3: Operational Risk
These are potential sources of losses that result from any sort of operational event; e.g. poorly-trained employees, a technological breakdown, or theft of information.
Banking Risk Type #4: Reputational Risk
Let’s say a news story breaks about a bank having corruption in leadership. This may damage their customer relationships, cause a drop in share price, give competitors an advantage, and more.
Banking Risk Type #5: Liquidity Risk
With any financial institution, there is always the risk that they are unable to pay back its liabilities in a timely manner because of unexpected claims or an obligation to sell long-term assets at an undervalued price.
Risk Management Practices in Banks
Banks must prioritize risk management in order to stay on top (and ahead) of the various critical risks they face every day. Risk management in banks also goes far beyond compliance, as banks must be on the lookout for strategic, operational, price, liquidity, and reputational risk. Staying on top of these risks demands a powerful and flexible bank risk management program.
The number of individual regulatory changes that financial institutions and banks must track on a global scale has more than tripled since 2011. There are millions of proposed rules and enforcement actions across multiple jurisdictions that organizations must follow. This requires regulatory change management to be a prominent practice within any bank’s risk management program.
Regulatory change management can be described in the simplest terms as “managing regulatory, policy and or procedures applicable to your organization for your industry.” Regulatory compliance can be a burdensome and costly task for financial institutions, so it is critical that organizations have the appropriate processes in place to identify changes to existing regulations as well as new regulations that impact the ability of the organization to achieve objectives. It is equally important that organizations are informed of any potential consequences or fines should they not meet the regulation.
Once a regulatory change has been made, it is essential for organizations to assess how they will implement the respective changes to their current policies, processes, and training sessions. As changes are implemented, organizations should begin tracking compliance with the updated regulation going forward.
Bonus Material: Financial Risk Assessment Template
Risk Management Process in Banking Industry
Having a clear, formalized risk management plan brings additional visibility into consideration. Standardizing risk management makes identifying systemic issues that affect the entire bank simple. The ideal risk management plan for a bank serves as a roadmap for improving performance by revealing key dependencies and control effectiveness. With proper implementation of a plan, banks ultimately should be able to better allocate time and resources towards what matters most.
Size, brand, market share, and many more characteristics all will prescribe a bank’s risk management program. That being said, all plans should be standardized, meaningful, and actionable. The same process for defining the steps within your risk management plan can be applied across the board:
Risk Identification In Banks
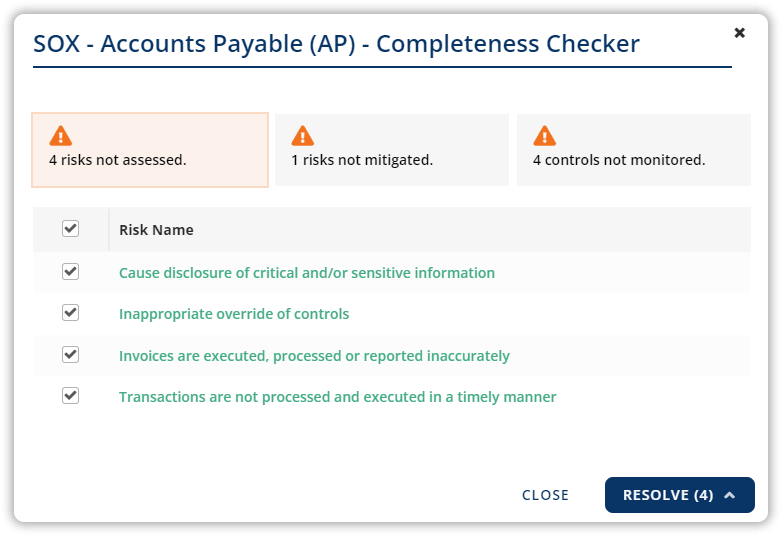
Banks must create a risk identification process across the organization in order to develop a meaningful risk management program. Note that it’s not enough to simply identify what happened; the most effective risk identification techniques focus on root cause. This allows for identification of systemic issues so that controls can be designed to eliminate the cost and time of duplicate effort.
Assessment & Analysis Methodology
Assessing risk in a uniform fashion is the hallmark of a healthy risk management system. It’s important to be able to collect and analyze data to determine the likelihood of any given risk and subsequently prioritize remediation efforts.
Mitigate
Risk mitigation is defined as the process of reducing risk exposure and minimizing the likelihood of an incident. Top risks and concerns need to be continually addressed to ensure the bank is fully protected.
Monitor
Monitoring risk should be an ongoing and proactive process. It involves testing, metric collection, and incidents remediation to certify that the controls are effective. It also allows for addressing emerging trends to determine whether or not progress is being made on various initiatives.
Connect
Creating relationships between risks, business units, mitigation activities, and more paints a cohesive picture of the bank. This allows for recognition of upstream and downstream dependencies, identification of systemic risks, and design of centralized controls. Eliminating silos eliminates the chances of missing critical pieces of information.
Report
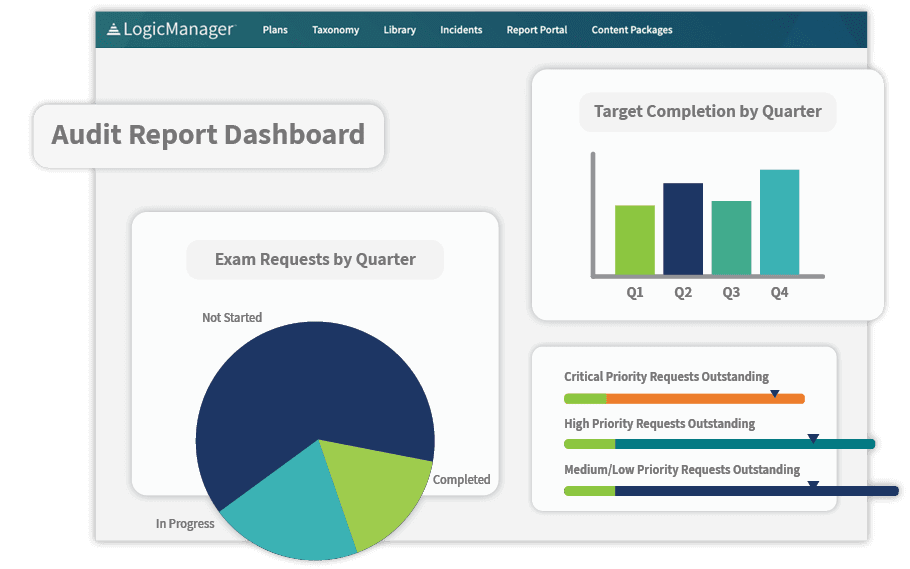
Presenting information about how the risk management program is going – in a clear and engaging way – demonstrates effectiveness and can rally the support of various stakeholders at the bank. Develop a risk report that centralizes information and gives a dynamic view of the bank’s risk profile.
ERM Software for Banks
The best way to begin the process of developing a sound banking risk management plan is by using enterprise risk management software. At LogicManager, we transform how you think about risk. Our platform is designed to alleviate the pain points in your bank’s ERM processes so that you can focus on aligning and achieving operational and strategic goals.
LogicManager’s risk management software for banks and expert advisory services provide a risk-based framework and methodology to accomplish all of your governance activities, while simultaneously revealing the connections between those activities and the goals they impact.
Risk Management in Banking Conclusion
Whether you are managing risks defined by the OCC, CFPB, FDIC, or any of the other many regulatory agencies, it’s important to think of risk management in banking as helping you accomplish more than just compliance. LogicManager’s solutions are designed to meet the needs of your unique and dynamic industry.